The remains of more than 1,700 victims have already surfaced, twice as many as expected
Report from Info Libre, by Angel Munarriz, Seville — January 6, 2023 7:39 p.m. @angel_munarriz (translation and editing for publication here, also Footnotes and Glossary by D.Breatnach)
The mass graves in the Seville cemetery are a puzzle. Historiographical research has concluded that thousands and thousands of victims of Francoism lie dumped without order or recognition, but there is hardly full certainty of a few hundred names registered in the municipal registry.
What is underground is a sordid totum revolutum1 of bones of those shot right there and on nearby walls, of those killed in prisons and concentration camps or in confrontations with the rebel troops, or of victims of hunger and poverty who were was buried free of charge along with those who suffered repression.
Today the puzzle is still far from complete; it will probably never be so, because part of the mission of the placing of graves in the San Fernando cemetery was to erase the traces of the crime.
But some pieces are beginning to fit. It is even possible already to glimpse some forms. What is observed goes beyond any hypothesis.
Not everything in this story is summed up in numbers, because behind each number there is a human being. But numbers are essential to understand its dimension.
There they go: the search in the mass graves of the Franco regime led by the Seville City Council is now extended to more than 4,000 possible victims, according to the calculations of the consistory itself, based on historiographical sources.
In the first excavated burial, Pico Reja, the remains of more than 1,700 victims have already surfaced, twice as many as expected, making it “the largest open mass grave in Western Europe since Srebrenica”, as the City Council highlights.
In the second, called Monumento, pending opening, there could be more than 2,600. The horror revealed in what was the fiefdom of Gonzalo Queipo de Llano2 seems to have no end.
Overflowing forecasts in Pico Reja
The exhumation work in the Pico Reja grave, which began a little less than two years ago, is nearing completion.
“The idea [of the City Council] is to carry out an act of symbolic closure of the pit before the end of January. We are going to do everything possible,” explains Juan Manuel Guijo, director of the excavation, which is in charge of the science society Aranzadi, a benchmark in this field.
Guijo is not certain about the deadlines.”The pit must be left clean, without remains,” he says. In addition, “a huge amount of funerary material is coming out.”
The anthropologist uses scientific jargon: “Huge amount of funerary material.” They are human bones.
The initial forecast for the number of deaths was just over 1,100, of which between 850 and 900 would be victims of Franco’s repression, according to the City Council. But reality has broken any forecast.
Guijo advances to InfoLibre the figures as of December 30: the remains of 8,600 individuals have been located, almost eight times more than previously thought; of these, 1,718 are victims of the Franco regime, around twice as many as expected.
The two figures, says Guijo, “will be exceeded” at the end of the excavation.
“We can reach 9,000 people exhumed. All this was impossible to foresee. It is beyond any possible forecast,” he says.
The mayor of Seville, Antonio Muñoz (PSOE), has said it in other words: “The reality was much worse than what was estimated in the initial forecasts.”
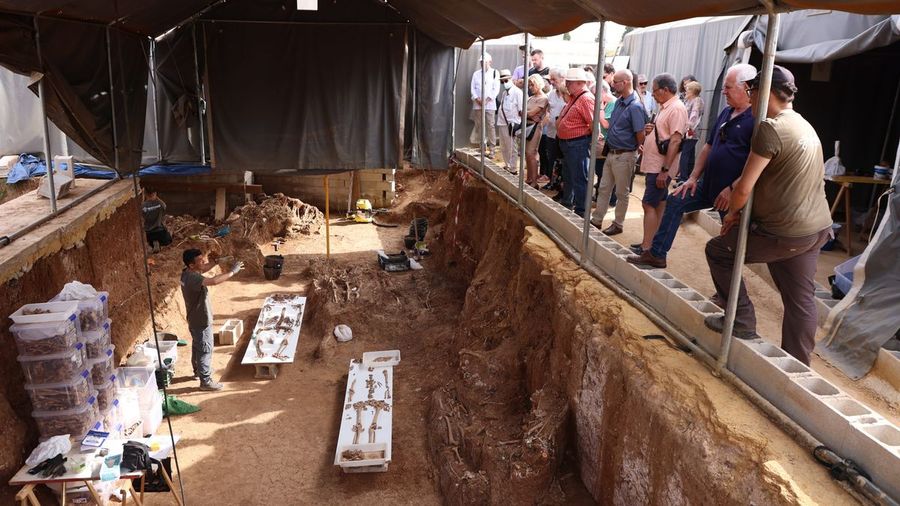

An explanation? The grave “was not filled up shortly after the coup, as was thought, but was open until 1940, or at least it was opened punctually in 1940,” explains Councilor Juan Tomás de Aragón.
The remains –wires and shackles– or the posture allow us to conclude that a victim was tied up, either with the wrists together or with the hands behind the back. Clips found appeared to hold several in a row with rope or wire.
The skull is the most frequent area of impact of the projectile, especially from behind, but also on the face. There is an abundance of long-arm projectiles used for the Mauser rifle, as well as short-arm bullets, mainly 9 mm.
In addition to the unmistakable bullet holes, there are “simple” fractures that point to “illtreatment” and “cruelty,” Guijo explains. The extreme fragmentation, mutilation, shrapnel and grenade remains seem to be attributable to “high energy trauma”, typical of combat.
500 families waiting: from Blas Infante to Horacio Gómez
One of the pieces of the puzzle fell into place in June.
The technicians confirmed the existence of evidence that certifies the remains of at least thirty of the victims who were members of what is known as the Mining Column, a group of volunteer fighters from the Huelva mining area that arrived in Seville bringing dynamite.
The characteristics of some burials –bodies without a coffin, grouped and face down– and the evidence that they had been retaliated against –shots to the neck, ties, perimortem fractures– allowed, together with some specific findings, to outline the hypothesis that they were members of the Miners Column.
There was a way to confirm it. How? These workers breathed, drank and ate in a mining environment without current security measures, so there could be a transfer of heavy metals to their bodies.
Indeed, the analyses carried out at the University of Santiago de Compostela have ratified it.
Much remains to be confirmed. Some 500 relatives have offered DNA samples, which must be compared with the remains of the victims, especially femurs, with signs of repression. You can’t always. There are more than 300 victims who do not present viable skeletal remains.
They are practically pulverized. This, added to the fact that the percentage of identifications with respect to the total number of bodies exhumed in this type of work is usually around 10%, caution is advised.
This same month of December, Horacio Hermoso, son of the former mayor of the city of the same name, a member of the Republican Left, assassinated in September 1936, died. Horacio Jr. gave his DNA, but did not arrive in time to see the end of the remains matching process.

Among the relatives who are still waiting is Estanislao Naranjo, grandson of Blas Infante, considered the father of Andalusianism, murdered in August 1936. “Things are going slowly, because it is a difficult grave,” he says.
Do you see the identification of his grandfather as possible? “In theory, yes. Due to the dates, they had to throw it into that pit. Now, it is difficult to know who was victimised and who was not. If the bullet hit a bone, you can see it. If it only touched soft parts, no,” he says.
Historical investigations maintain that, in addition to Infante, the remains of other political and union figures of the time rest in the grave, as well as loyal soldiers – Captain Ignacio Alonso – and assault guards3.
Councilor Juan Tomás de Aragón (PSOE) emphasises that all the victims will have a “dignified burial.” The City Council will build a memorial and a columbarium over the grave.
The Mayor tries not to generate excessive expectations about the identifications, so as not to pivot on this last phase the success or failure of the works. The truth is that the exhumation of Pico Reja has involved much more than exhumations and possible identifications.
For example, it has led to the making of several documentaries, such as Pico Reja. The truth that the earth hides. Students from schools, institutes and universities, from Seville and abroad, have organized visits to the work area.
Numerous university researchers have taken an interest in the process.
Monumento: the emblematic grave of Cruz de Lolo
The opening will not be limited to Pico Reja. The City Council plans to put out to tender in 2023 the excavation work for a second grave. It is known as the Alpargateros or Monumento pit.
According to available studies, it was open between September 1936 and January 1940 and no less than 7,440 bodies of deaths from different causes were deposited there, of which some 2,613 would be victims of Francoism.
Among them are believed to be the eight convicted of a plot against General Gonzalo Queipo de Llano, during which Concha Morón was arrested as part of The Resistence in Sevilla. An attempt to overthrow Queipo (Aconcagua, 2013).
Carmen Díaz may also be there, sister of the general secretary of the PCE, José Díaz.
If the forecasts of victims of the Franco regime in the Monumento pit are met, the total of the two burials would easily exceed 4,000. After Pico Reja‘s surprise, no one dares to say so. Perhaps, says the archaeologist Guijo, bodies attributed to Monumento were in Pico Reja.

Graves (and more matters) pending
The City Council trusts that the collaboration of the Diputación, the Junta de Andalucía4 and the Government in Pico Reja, where they have invested 1.5 million euros, will be repeated in Monumento, so called because of a commemorative monument raised there in 2003 by initiative of the Association of former Political Prisoners and Victims of the Franco regime.
Almost everyone who remembers that in this entire area crime reached inhuman levels hovers around the Monument pit.
In addition to the monument, in its paved area there is a cross placed by a communist blacksmith in the early 50s, tolerated by the authorities and known as the Cruz de Lolo. For the rest, no one would say. Seville has lived for decades in a democracy with back turned to the memory of its horrors.
The remains of Blas Infante, named by Parliament “father of the Andalusian homeland”, was not begun to be searched for until 2020.
Those of Queipo, head of the repression in southern Spain, the coup leader who called for “raping Reds”, have only recently left the place of honour they occupied in the basilica of La Macarena,5 in compliance with a state law.
This was without the confraternity with the most members in the city acting on its own initiative. Apart from this exhumation, the honours granted to him still stain the city.
Councilor Juan Tomás de Aragón highlights the “normality” with which the exhumation of Pico Reja has been carried out, which he is sure will be repeated in the Monumento.
“Nobody has clutched their heads in their hands. People are more intelligent and mature than is sometimes thought,” he says. He believes that the key has been respect: “We have not hidden what we were doing, nor have we used it to confront anyone.”
There are more graves in the complex, in addition to Pico Reja and Monumento. Antigua –delimited and where it has been verified that there are no remains of victims, according to the councilor–, Rotonda de los Fusilados, Disidentes y Judíos, some extensions of filled graves…
“Francoism never admitted that there were graves, that’s why they were known by popular names. If it had admitted them, they would be called San Rafael, Santa Águeda …”, explains Juan Morillo, a reference to the memorialist movement in Andalusia.
He sees the exhumation process of Pico Reja as “exemplary”, but at the same time stresses: “All this, it must be remembered, has been done due to the pressure of family members and associations. No party had it on their pprogram.
“Memory continues to be the great democratic deficit in this country, where there are still unopened graves and streets with Francoist names”.
The City Council does not plan to disinter these graves, at least not while the largest ones are open. According to the available evidence, they have much fewer victims than Pico Reja and Monumento.
Comment
by Diarmuid Breatnach
It is important to note that most of the executions by the fascist-military forces during the Civil War took place outside combat zones, in which the fascist-military were in no danger whatsoever. They were punishing not only soldiers of the Second Republic but political activists and functionaries.
This is in contrast to the much lower number of executions in the zones under control of the Republic and, furthermore, as their authorities exercised greater control, the executions were reduced considerably.
Many executions also took place after the fall of the Republic and the terrible conditions of the vastly overcrowded jails and prison camps added their contribution to the fascist military harvest. Their purpose was revenge, deterrence of others and elimination of a democratic generation.
Generations growing up afterwards knew little of the extent of the horror unless informed by their family and communities, though may of these in turn felt obliged to remain silent unless they – or their sons and daughters – were to also become victims.
The subject is not taught in the schools and during the Dictatorship children were taught and expected to salute the icon of the Dictator Franco.
Unlike in Germany and even in Portugal, fascism was never defeated in the Spanish state and the Transition from Dictatorship brought the military, police, judges, civil servants, media moguls, university dons and Catholic hierarchy safely into the new “democracy”.
In addition, most of those who seized land, buildings, machinery and equipment, vehicles and personal wealth of the victims of the coup and war, were allowed to keep them
As Juan Morillo reminds us (see article), it is not the Spanish State that has pushed the process of disinterment and documentation of these mass graves, but relatives, communities and concerned citizens. And for a long time it was even dangerous to pursue such activities.
Fascism remains alive and strong in the Spanish state.
End.
Footnotes
1A total jumble
2Gonzalo Queipo de Llano y Sierra (5 February 1875 – 9 March 1951) was a Spanish military leader who rose to prominence during the July 1936 coup and soon afterwards the Spanish Civil War and the White Terror that followed. Capturing Seville with a force of at least 4,000 troops and ordering mass killings, he later made ridiculous claims, including that the city had been defended by 100,000 armed communists and that the fascist military troops had taken the city with as few as fifteen men. Quiepo de Llano publicly called for women of the Republican opposition to be raped.
3From Wikipedia: The Cuerpo de Seguridad y Asalto (English: Security and Assault Corps) was the heavy reserve force of the blue-uniformed urban police force of Spain during the Spanish Second Republic. (for more, see Glossary)
4The governing body of that ‘autonomous’ region.
5See Glossary.
References
Original article: https://www.infolibre.es/politica/busqueda-fosas-comunes-franquismo-sevilla-amplia-4-000-victimas_1_1394807.html
https://www.infolibre.es/politica/tributos-queipo-sobreviven-sevilla-gracias-iglesia_1_1355792.html
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gonzalo_Queipo_de_Llano
Glossary
Andalusia: One of the ‘autonomous regions’ of the Spanish state, large southern region, from Al Andalus, province of the Moorish conquest of large areas of the Spanish state. After the Canary Islands it was the easiest for Franco’s troops to reach from the Spanish colony in North Africa; its defenders lacked time to prepare and did not last long against a well-armed and large invasion force.
Assault Guards (From Wikipedia): The Cuerpo de Seguridad y Asalto (English: Security and Assault Corps) was the heavy reserve force of the blue-uniformed urban police force of Spain during the Spanish Second Republic.The Assault Guards were special police and paramilitary units created by the Spanish Republic in 1931 to deal with urban and political violence. Most of the recruits in the Assault Guards were ex-military personnel, many of which were veterans.
At the onset of the Spanish Civil War there were 18,000 Assault Guards. About 12,000 stayed loyal to the Republican government, while another 5,000 joined the rebel faction.[1] Many of its units fought against the Franco supporting armies and their allies. Their siding with the former Spanish Republic’s government brought about the disbandment of the corps at the end of the Civil War. The members of the Guardia de Asalto who had survived the war and the ensuing Francoist purges were made part of the Policía Armada, the corps that replaced it.
Diputación: Regional administrative body in most regions of the Spanish state.
Izquierda Republicana Republican Left (from Wikipedia, translated): Izquierda Republicana (IR) was a Spanish left-wing republican political party founded by Manuel Azaña in 1934. It played a prominent role during the Second Spanish Republic and in the moments preceding the start of the Civil War. Azaña became President of the Republic between 1936 and 1939. During the Franco dictatorship the party practically disappeared from the political scene except in the sphere of Republican exile in Mexico, where it continued to have some activity. As of 1977 it was reconstituted in Spain again, although without having the (degree of) importance of the historical party.
La Macarena: Basilica of Nuestra Señora de la Esperanza Macarena (Our Lady of Hope of Macarena, base of the Holy Week Confraternity of that Catholic church. The procession on the early morning of Good Friday is one of the largest, most popular, and fervent in the whole of the Spanish state. The wooden statue of Our Lady of Hope of Macarena dates from the 17th century.
PCE: Partido Comunista de España (Communist Party of Spain) is a communist party, banned by Franco but supported the Transition from the Dictatorship and the monarchist Constitution, subsequently experiencing a number of splits. Comisiones Obreras (CCOO), one of the two main trade unions in the Spanish state, its associated trade union movement was the main underground workers’ element in forcing the change from dictatorship but is no longer under its control.
PSOE: Partido Socialista Obrero de España (Socialist Workers Party of Spain) is a social-democratic party, banned by Franco but supported the Transition from the Dictatorship and the monarchist Constitution, subsequently one of two main parties of government in the Spanish state, at the time of writing the senior member in coalition government with the Podemos party. Its associated trade union, Unión General de Trabajadores (UGT), is one of the two main trade unions in the Spanish state.






