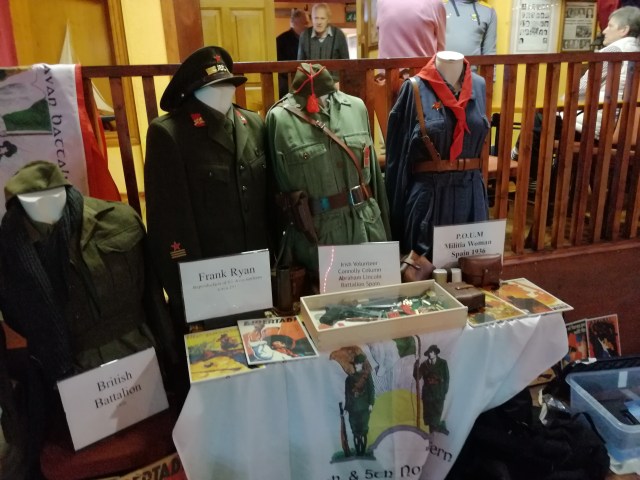
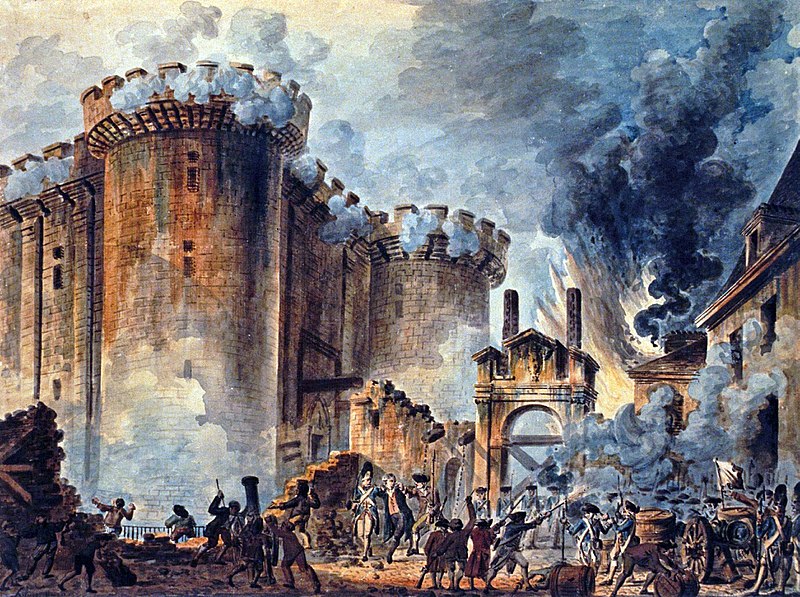
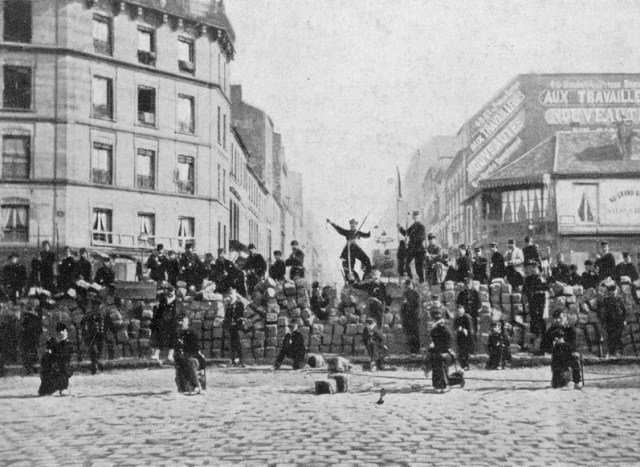(Traducción al castellano de bajo del inglés)
(Reading time: 5 minutes)
Diarmuid Breatnach
Racists and Fascists, posing as Irish “patriots”, malign migrants to Ireland and target them in racist propaganda. This is a fundamentally unpatriotic activity, flying against not only our own huge history of migration to other lands but also against the great history of migrants’ contribution to the struggle for Irish independence and socialism.
Of the Seven Signatories of the 1916 Proclamation of Independence, two were migrants and two more were sons of migrants.
Of the sixteen of the Rising executed by the English, two were migrants (Connolly and Clarke), another three were sons of migrants (Pearse brothers, Mac Donagh) and at least six bore family names of foreign ancestry (Casement, Ceannt, Clarke, Colbert, Kent, Plunkett).
Numerous migrants took part in the 1916 Rising, mostly from England and Scotland but also some from the USA, one from Argentina, another from Finland and yet another from Sweden).

(Design: Maria Castella; photo: B.Hoppenbrouwers)
Constance Markievicz (nee Gore-Booth), feminist, Irish Republican, Socialist, officer in the Irish Citizen Army, first woman elected to the British Parliament, first female Minister of the Dáil and first Labour Minister in the world, was born in England; she was sentenced to death in 1916 by the English but had her sentence commuted. Volunteer Eamon De Valera, a 1916 Rising garrison Commander, was born in the USA to an Irish mother and a Cuban father. The captain of the Asgard yacht that delivered the Mauser rifles for the 1916 Rising was an Englishman, Erskine Childers and among the crew were his wife Molly from the USA and Mary Spring Rice (born London). Childers fought in the War of Independence and the Civil War and was executed by the Irish Free State in 1922.
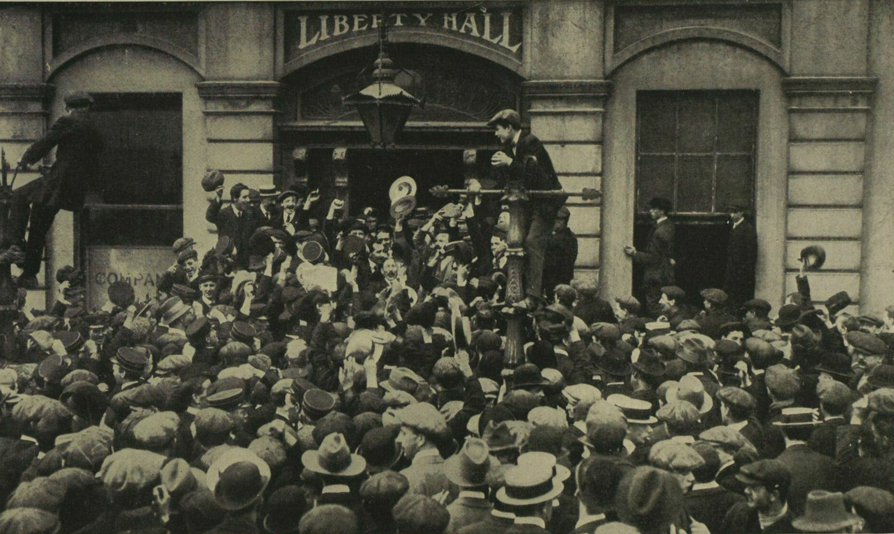
Jim Larkin, trade union organiser and Lockout resistance leader, who was in the USA during the Rising, was co-founder of the Irish Transport & General Workers’ Union and of the Irish Citizen Army, also of the Irish Labour Party. Larkin was born and raised in Liverpool and did not see Ireland until sent to Belfast by his England-based trade union.

(Image source: Internet)
A LONG HISTORY OF MIGRANT CONTRIBUTION TO IRISH STRUGGLES
The aforesaid should not surprise us as migrants have often participated in struggles for freedom and social progress in their adopted countries and they and their descendants have a long history of taking up those struggles in Ireland – often sacrificing their liberty and even their lives in doing so.
Patrick Sarsfield, a hero of the resistance to William of Orange in the army of James II was of Anglo-Norman descent (he was a prominent member of the Wild Geese and was killed in military service abroad in 1683).
Nearly all the leaders of the Society of United Irishmen, the first Republican revolutionary organisation of Ireland, were Protestants of various sects and descendants of migrants. Henry and Mary Joy McCracken were active in saving Irish traditional melodies; their ancestors were Huguenots (French Protestant refugees).
Henry Joy was executed publicly in Belfast by the English in 1798, his sister walking hand-in-hand with him to the gallows. General Henry Munro, another Antrim Unitedmen leader, also executed in 1798, was of Scottish descent.
Theobald Wolfe Tone, Anglican co-founder of the Unitedmen and often described as the “father of Irish Republicanism”, was also of Huguenot ancestry; he died in jail in Dublin, while his brother Matthew was hanged. Edward Fitzgerald, another leader of the Unitedmen who died of his injuries in a Dublin jail, was a Protestant and descendant of Norman invaders.
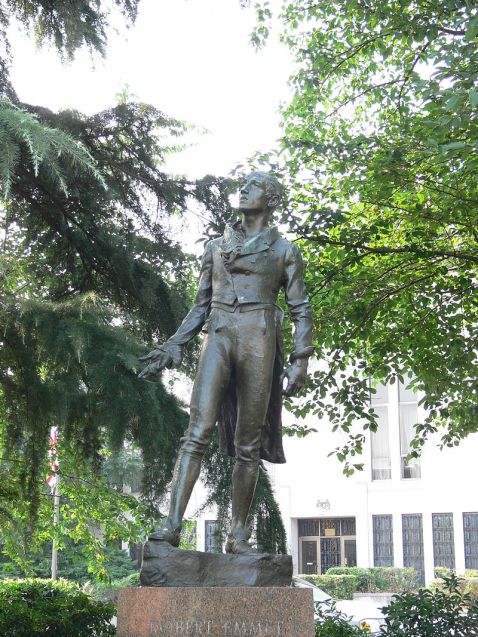
Robert Emmet, another famous United Irishman but martyred in 1803, bore a surname of English origin as did one of his prominent comrades, Thomas Russell (“The Man from God Knows Where”), also executed by the English that year.
The Young Irelanders were the next Irish Republican organisation in history, their leaders a mixture of Protestant and Catholic background. One of the most famous was Thomas Davis, the son of a Welshman in the British Army and an Irish woman descended from Irish chieftain Ó Súilleabháin Béara.
Davis founded The Nation newspaper and composed a number of poems and songs, some of the latter being still sung today (e.g A Nation Once Again and The West’s Awake).
James Stephens and a handful of others founded the Irish Republican Brotherhood on 17th March 1858 in Dublin, the third Irish Republican organisation in Irish history and the life of which extended into the 1920s. Stephens is a family name of Anglo-Norman origin.
John Devoy of the Irish Republican Brotherhood in the USA, who was very active in supporting the 1916 Rising and the War of Independence, carried a family name of Welsh origin. Wales was also the likely origin of Michael Davitt’s family name, he who was chief organiser of the Land League’s base membership.
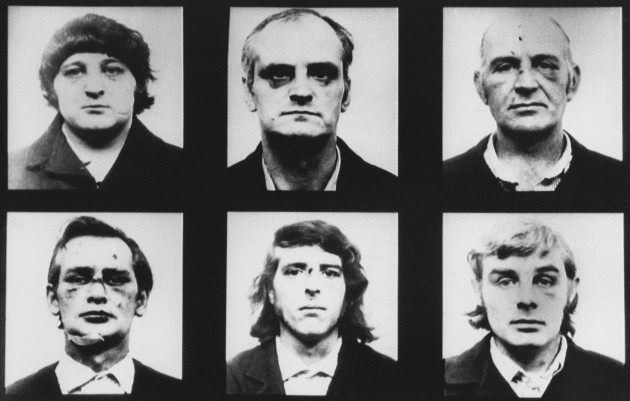
Volunteers Terence McSwiney and Kevin Barry, who both died in the same week in 1920, the first on hunger strike and the second hanged by the English, had family names of foreign origin.
WHO IS NOT A DESCENDANT OF MIGRANTS?
Of course, we are ALL descendants of migrants. The earliest date for human occupation of parts of Ireland has been calculated as being 7,000 BCE.
Since the earliest date given for the existence of homo sapiens is 300,000 years ago in the Horn of Africa (although throwing spears in Germany have been assessed as being between 380,000 and 400,000 years old), it follows that human settlement in Ireland was comparatively late and that all Irish are descended from migrants.
Stone age people arrived first, then the metal workers of bronze, followed by people of Celtic culture working iron.
Subsequently Ireland saw influxes of other groups, from Norse and Danes when they began to settle in parts of Ireland, followed by their cousins based in Normandy (and mercenaries they brought with them), then English and so on.
Religious groups seeking security such as Jews or fleeing persecution, for example the Huguenots, also entered at various times. Just a study of family names common in the Ireland of today reveals some of those ancestries.
The Norse, Danes, Normans and early English came as invaders, some more came subsequently as planters and many others came just to make a living in Ireland, like most migrants of today.
But descendants of all those groups, including of invaders and planters, contributed to and even led the struggle for Irish independence and social progress. Not only that but a significant number of those who arrived as migrants themselves took a stand for Irish independence, some of them paying the ultimate price.

(Design: Maria Castella; photo: B.Hoppenbrouwers)
CONCLUSION
Far from being “patriotic”, maligning migrants simply for being migrants is counter to the history of the general struggle for Irish independence and of Irish Republicanism in particular. It actually undermines the unfinished struggle for Irish independence and unification as well, of course, as the struggle of the working people for socialism.
End.
TRADUCCIÓN AL CASTELLANO:
LOS INMIGRANTES EN LA HISTORIA IRLANDESA
Los racistas y fascistas, haciéndose pasar por “patriotas” irlandeses, atacan a los inmigrantes en Irlanda en su propaganda racista. Esta actividad es fundamentalmente antipatriótica, que vuela no solo contra nuestra enorme historia de migración a otras tierras sino también contra la gran historia de la contribución de los inmigrantes a la lucha por la independencia y el socialismo irlandés.
De los Siete Signatarios de la Proclamación de Independencia de 1916, dos eran inmigrantes y un tercero era hijo de un inmigrante. De los dieciséis del Azamiento ejecutados por los ingleses, dos eran inmigrantes (Connolly y Clarke), otros dos eran hijos de inmigrantes (hermanos Pearse) y al menos seis tenían apellidos de ascendencia extranjera (Casement, Ceannt, Clarke, Colbert, Kent, Plunkett). Numerosos inmigrantes participaron en el Alzantamiento de 1916, principalmente de Inglaterra y Escocia, pero también algunos de los EEUU, uno de Argentina, otro de Finlandia y otro de Suecia).
Constance Markievicz (soltera Gore-Booth), feminista, republicana irlandesa, socialista, oficial del ejército ciudadano irlandés y primera mujer elegida para el Parlamento británico, la primera mujer ministra del Parlamento irlandés y primera ministra femenina de trabajo del mundo, nació en Inglaterra; fue condenada a muerte en 1916 por los ingleses, pero la conmutaron la pena. El voluntario Eamon De Valera, un comandante de la guarnición del Azamiento de 1916, nació en los Estados Unidos de una madre irlandesa y un padre cubano. El capitán del yate Asgard que entregó los fusiles Mauser para el Alzamiento de 1916 era un inglés, Erskine Childers y entre la tripulación estaban su esposa Molly (de los Estados Unidos) y Mary Spring Rice (nacida en Londres). Childers luchó en la Guerra de la Independencia y la Guerra Civil y fue ejecutado por el Estado Libre de Irlanda en 1922.
Jim Larkin, organizador sindical y líder de la resistencia al Cierre Patronal, que estuvo en los EEUU durante el Alzamiento, fue cofundador del Sindicato de Trabajadores Generales y de Transporte de Irlanda y del Ejército de Ciudadanos de Irlanda, también del Partido Laborista. Larkin nació y creció en Liverpool y no vio Irlanda hasta estar enviado a Belfast por su sindicato con sede en Inglaterra.
UNA LARGA HISTORIA DE CONTRIBUCIÓN MIGRANTE A LAS LUCHA IRLANDESA
Lo anterior no debería sorprendernos, ya que los migrantes a menudo han participado en luchas por la libertad y el progreso social en sus países adoptados y ellos y sus descendientes tienen una larga historia de asumir esas luchas en Irlanda, a menudo sacrificando su libertad e incluso sus vidas al hacerlo. .
Patrick Sarsfield, un héroe de la resistencia a Guillermo Naranja en el ejército de Jaime II de Gran Bretaña, era de ascendencia anglo-normanda (era un miembro destacado de los “Gansos Silvestes” y fue asesinado en el servicio militar en el extranjero en 1683).
Casi todos los líderes de la Sociedad de Irlandeses Unidos, la primera organización revolucionaria republicana de Irlanda, eran protestantes de varias sectas y descendientes de inmigrantes. Henry y Mary Joy McCracken fueron activos en salvar las melodías tradicionales irlandesas; sus antepasados eran hugonotes (refugiados protestantes franceses). Henry Joy fue ejecutado públicamente en Belfast por los ingleses en 1798, su hermana caminó de la mano con él hacia la horca. El general Henry Munro, otro líder de Los Irelandeses Unidos de Antrim, también ejecutado en 1798, era de ascendencia escocesa. Theobald Wolfe Tone, cofundador anglicano de los Irelandeses Unidos y a menudo descrito como el “padre del republicanismo irlandés”, también era de ascendencia hugonote; murió en la cárcel de Dublín, mientras que su hermano Matthew fue ahorcado. Edward Fitzgerald, otro líder de los Irelandeses Unidos que murió por sus heridas en una cárcel de Dublín, era protestante y descendiente de invasores normandos.
Robert Emmet, otro famoso de los Irelandeses Unidos pero martirizado en 1803, tenía un apellido de origen inglés, al igual que uno de sus camaradas prominentes, Thomas Russell (“The Man from God Knows Where”), también ejecutado por los ingleses ese año.
Los Jóvenes Irlandeses fueron la próxima organización republicana irlandesa, sus líderes una mezcla de antecedentes protestantes y católicos. Uno de los más famosos fue Thomas Davis, hijo de un galés en el ejército británico y una mujer irlandesa descendiente del jefe irlandés Ó Súilleabháin Béara. Davis fundó el periódico The Nation y compuso una serie de poemas y canciones, algunas de las cuales todavía se cantan hoy (por ejemplo, A Nation Once Again y The West’s Awake).
James Stephens y un puñado de otros fundaron la Hermandad Republicana Irlandesa el 17 de marzo de 1858 en Dublín, la tercera organización republicana irlandesa en la historia de Irlanda y cuya vida se extendió hasta la década de 1920. Stephens es un apellido de origen anglo-normando.
John Devoy, de la Hermandad Republicana Irlandesa en los EEUU, que fue muy activo en el apoyo al Alzamiento de 1916 y la Guerra de la Independencia, llevaba un apellido de origen galés, lo qual también fue el origen probable del apellido de Michael Davitt, el principal organizador de la membresía base de la Liga de la Tierra.
Los Voluntarios del IRA Terence McSwiney y Kevin Barry, quienes murieron en la misma semana en 1920, el primero en huelga de hambre y el segundo ahorcado por los ingleses, tenían apellidos de origen invasor.
¿QUIÉN NO ES UN DESCENDENTE DE MIGRANTES?
Por supuesto, TODOS somos descendientes de migrantes. La fecha más temprana para la ocupación humana de partes de Irlanda se calculó ser en 7,000 aC. Dado que la fecha más temprana dada para la existencia del homo sapiens es hace 300,000 años en lo que hoy es Marruecos, se deduce que el asentamiento humano en Irlanda fue relativamente tarde y que todos los irlandeses son descendientes de migrantes.
Primero llegaron personas de la edad de piedra, luego los trabajadores metalúrgicos de bronce, seguidos por gente de la cultura celta que trabajaban el hierro. Posteriormente, Irlanda vio la afluencia de otros grupos, de nórdicos y daneses cuando comenzaron a establecerse en partes de Irlanda, seguidos por sus primos con sede en Normandía (y mercenarios que trajeron con ellos), luego ingleses, etc. Los grupos religiosos que buscaban seguridad como los judíos o huían de la persecución, por ejemplo los hugonotes, también ingresaron en varios momentos. Un estudio de apellidos comunes en la Irlanda de hoy basta para revelar algunos de esos antepasados.
Los nórdicos, daneses, normandos y los primeros ingleses llegaron como invasores, algunos más llegaron posteriormente como plantadores y muchos otros vinieron para ganarse la vida en Irlanda, como la mayoría de los inmigrantes de hoy. Pero los descendientes de todos esos grupos, incluidos los invasores y plantadores, contribuyeron e incluso lideraron la lucha por la independencia de Irlanda y el progreso social. No solo eso, sino que un número significativo de los que llegaron como migrantes tomaron posición por la independencia de Irlanda, algunos de ellos pagando el precio final.
CONCLUSIÓN
Lejos de ser “patriótico”, difamar a los migrantes simplemente por ser migrantes es contrario a la historia de la lucha general por la independencia de Irlanda y del republicanismo irlandés en particular. De hecho, mina la lucha todavía inconclusa por la independencia y la unificación irlandesa, así como, por supuesto, la lucha de los trabajadores por el socialismo.
Fin.